- Visibility 451 Views
- Downloads 44 Downloads
- Permissions
- DOI 10.18231/j.jco.2024.016
-
CrossMark
- Citation
Bonded lingual spur to intercept thumb sucking habit: A clinical pearl
- Author Details:
-
Surendra Kumar Sewda *
-
Dinesh Chander Chaudhary
-
Sukhbir Singh Chopra
-
Dhruv Jain
-
Vivek Kumar Thakur
Abstract
Thumb sucking is usually treated with fixed and removable palatal cribs and lingual spurs. Bonded lingual spurs were envisioned and designed based on the principles of conventional Orthodontic spurs. Bonded lingual spur has some apparent advantages over banded lingual spur such as no need of molar banding, small size, low cost, superior esthetics, less laboratory preparation, easy insertion and reduced clinical time. This case pearl describes an innovative method of fabrication of bonded lingual spur.
Introduction
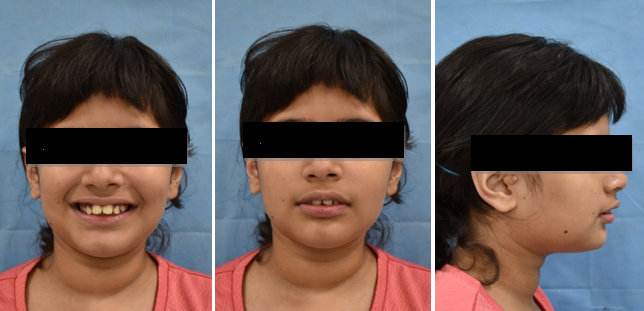
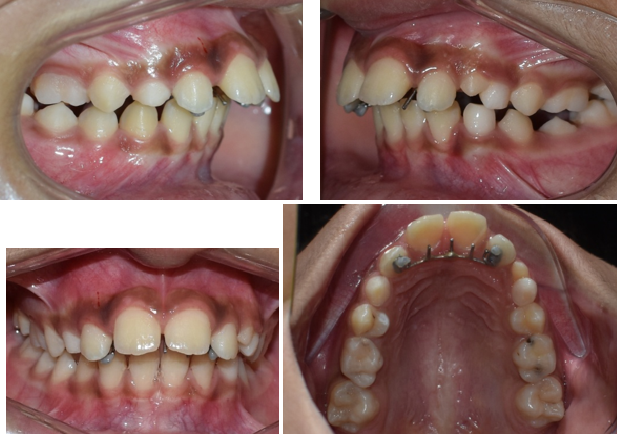
Thumb sucking is a common deleterious oral habit in young children; it affects almost 45% of the young population of the world from birth through adolescence. Prolonged thumb sucking may cause reduced vertical growth of the anterior maxillary alveolar processes which creates an anterior open bite, proclination of upper incisors as a result of the horizontal force created by the thumb/finger which may lead to increased overjet, posterior crossbite and retroclination of lower incisors.[1], [2] Self correction of this malocclusions may occur if the thumb sucking habit is discontinued before 4 years. Multiple modalities have been applied in the management of these habits. Fixed (Banded & Bonded) and removable palatal cribs and lingual spurs constitute the popular line of treatment to intercept habit of thumb sucking. [3] Here, we present a very simple and cost effective innovative method of bonded lingual spurs fabrication to intercept the habit of thumb sucking.
Fabrication of bonded lingual spurs
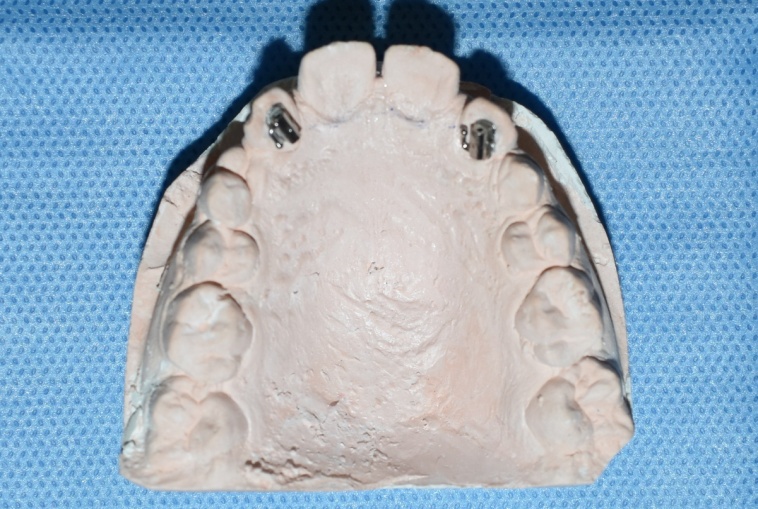
The first step is to prepare the working cast after taking the maxillary arch impression with irreversible hydrocolloid (Alginate) impression material and apply separating media over it. Bondable molar tubes are bonded with composite on the lateral incisors as shown in [Figure 1].
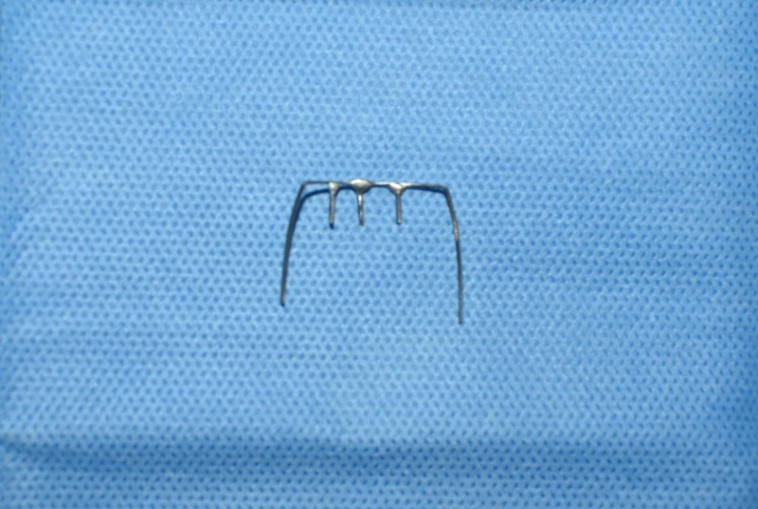
Lingual Spur are fabricated by soldering 3-4 spurs over 0.016 x 0.022 or 0.017 x 0.025 Stainless steel shaped along the palatal surface of incisors. The free ends are bent considering their insertion into the bonded molar tubes as shown in [Figure 2].
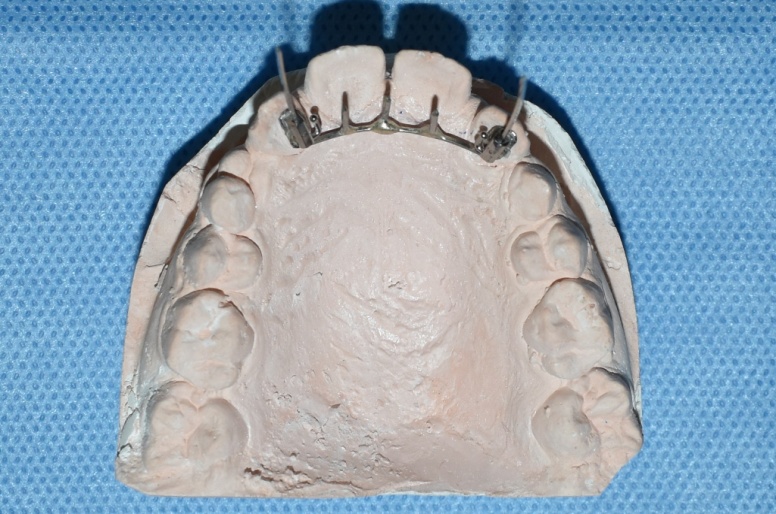
Then Lingual Spur is inserted into bonded molar tubes on the palatal surface of lateral incisors on the working cast as shown in [Figure 3].
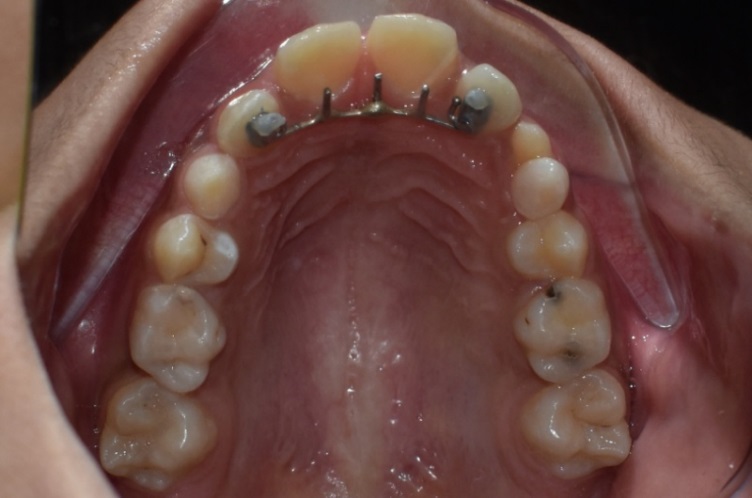
Finally, this bonded lingual spur assembly is taken and bonded intraorally on palatal surface of maxillary lateral incisors and the ends of the bonded lingual spurs are covered with composite to stabilize the bonded lingual spurs into bonded molar tubes as shown in [Figure 4].
Discussion
This Bonded lingual spur is indicated to intercept the habit of thumb sucking and tongue thrusting. It can be used in patient with anterior open bite and anterior spacing for tongue training. It has some added advantages over the other bonded lingual spur such as smaller in size, low cost, superior esthetics, no of spurs can be increased or decreased as required, easy to insert, reduced chair side time, versatile in fabrication; as it can be fabricated using rectangular stainless steel (0.016 x 0.022 SS, 0.017 x 0.025 SS, 0.019 x 0.025 SS) or round stainless steel.
Source of Funding
None.
Conflicts of Interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
References
- Garattini G, Crozzoli P, Valsasina A. Role of prolonged sucking in the development of dento-skeletal changes in the face-Review of the literature. Mondo Ortod. 1990;15(5):539-50. [Google Scholar]
- Larsson E. Artificial sucking habits: etiology, prevalence and effect on occlusion. Int J Orofacial Myology. 1994;20:10-21. [Google Scholar]
- Moore NL. Suffer the little children: Fixed intraoral habit appliances for treating childhood thumbsucking habits: a critical review of the literature. International Journal of Orofacial Myology. 2000;28(1):6-38. [Google Scholar]
How to Cite This Article
Vancouver
Sewda SK, Chaudhary DC, Chopra SS, Jain D, Thakur VK. Bonded lingual spur to intercept thumb sucking habit: A clinical pearl [Internet]. J Contemp Orthod. 2024 [cited 2025 Oct 10];8(1):96-98. Available from: https://doi.org/10.18231/j.jco.2024.016
APA
Sewda, S. K., Chaudhary, D. C., Chopra, S. S., Jain, D., Thakur, V. K. (2024). Bonded lingual spur to intercept thumb sucking habit: A clinical pearl. J Contemp Orthod, 8(1), 96-98. https://doi.org/10.18231/j.jco.2024.016
MLA
Sewda, Surendra Kumar, Chaudhary, Dinesh Chander, Chopra, Sukhbir Singh, Jain, Dhruv, Thakur, Vivek Kumar. "Bonded lingual spur to intercept thumb sucking habit: A clinical pearl." J Contemp Orthod, vol. 8, no. 1, 2024, pp. 96-98. https://doi.org/10.18231/j.jco.2024.016
Chicago
Sewda, S. K., Chaudhary, D. C., Chopra, S. S., Jain, D., Thakur, V. K.. "Bonded lingual spur to intercept thumb sucking habit: A clinical pearl." J Contemp Orthod 8, no. 1 (2024): 96-98. https://doi.org/10.18231/j.jco.2024.016
